Accounts receivable is indeed an asset. It represents money owed to a company by its customers for goods or services provided. Essentially, it Is like having money in the bank, just waiting to be collected.
The definition of accounts receivable (AR)
Accounts receivable (AR) refers to the money owed to a company by its customers for goods delivered or services rendered. It Is essentially a record of outstanding invoices awaiting payment. AR is a crucial aspect of a company’s finances, representing income that has been earned but not yet collected.
These outstanding balances are considered assets because they signify future cash inflows. While they may not be immediately available as cash, they contribute to the company’s overall financial health and liquidity. Efficient management of AR is essential for maintaining cash flow and sustaining business operations.
What are assets?
Assets encompass resources owned by a company that hold value and can generate future income:
- Tangible assets include physical items like inventory, vehicles, and real estate.
- Intangible assets represent non-physical items like patents, trademarks, and goodwill.
- Current assets are those expected to be converted into cash or used up within one year, such as cash, accounts receivable, and inventory.
Long-term assets provide benefits over an extended period, including property, equipment, and investments. Understanding assets is crucial for evaluating a company’s financial position and potential for growth.
Also Read: HOW TO ACCESS YOUR MASTER STRAWMAN ACCOUNT
What are liabilities?
Liabilities are financial obligations that a company owes to external parties:
- Examples include loans, accounts payable, and accrued expenses.
- They represent debts that must be repaid or settled through future actions or payments.
Liabilities are distinct from assets, which represent what a company owns, and equity, which reflects ownership. Understanding liabilities is essential for assessing a company’s financial health and obligations.
Is accounts receivable an asset?
Yes, accounts receivable is considered an asset in business accounting.
It represents money owed to a company by its customers for goods delivered or services rendered.
This asset reflects future cash inflows and contributes to the company’s financial health and liquidity.
Why is accounts receivable an asset?

Accounts receivable is classified as an asset because it represents money owed to a company by its customers.
This asset is valuable because it signifies future cash inflows and contributes to the company’s financial health and liquidity.
Efficient management of accounts receivable ensures timely collection, which is crucial for sustaining business operations and growth.
Is accounts receivable revenue?
Accounts receivable is not classified as revenue in business accounting practices.
Revenue is recognized when goods or services are provided, regardless of payment timing.
Accounts receivable, on the other hand, represents money owed by customers for products delivered or services rendered.
While it reflects pending payments, revenue is only recognized once payment is received, typically recorded in the income statement.
How businesses benefit from accounts receivable

Businesses benefit from accounts receivable in several ways. Firstly, it improves cash flow by ensuring timely collection of payments. Secondly, AR management provides insights into sales trends and customer behavior, aiding in informed decision making. Lastly, it assists in forecasting future cash flow, reducing administrative workload, and improving loan approval chances.
Improving cash flow through AR financing
AR financing, also known as factoring, offers businesses immediate cash flow solutions by selling unpaid invoices to third parties.
This approach enables companies to access funds tied up in AR, facilitating timely payment of expenses and investments in growth opportunities.
By converting outstanding invoices into cash, AR financing improves liquidity and ensures smooth business operations.
Assists in easy loan approvals
Efficient management of accounts receivable can enhance a company’s creditworthiness, making loan approvals smoother.
- A strong AR balance demonstrates consistent revenue and reliable customers.
- Lenders often review a company’s AR turnover ratio to gauge its financial health.
- Prompt payment collection reflects positively on a company’s ability to manage finances responsibly.
By maintaining healthy accounts receivable practices, businesses can increase their chances of securing loans and accessing additional capital for growth initiatives.
Provides insights into business operations
Analyzing accounts receivable offers valuable insights into business operations, aiding in informed decision-making.
Understanding customer payment behavior and sales trends helps identify revenue drivers and optimize business strategies.
This analysis of AR aging reports assists in managing cash flow effectively and refining collection strategies for improved financial health.
Helps in forecasting future cash flow
Accounts receivable management aids in forecasting future cash flow by analyzing payment histories and AR aging reports. This analysis helps predict incoming cash inflows and outgoing payments accurately.
Understanding customer payment patterns and sales trends enables businesses to anticipate future cash flow. Analyzing AR aging reports provides insights into outstanding invoices and expected payment timelines.
Reduces administrative workload
Efficient accounts receivable management reduces the administrative workload by automating invoicing and payment tracking processes. This streamlines tasks, saves time, and minimizes manual errors.
Automated reminders for overdue payments help in prompt follow ups, reducing the need for manual intervention and administrative tasks.
Moreover, implementing AR automation software simplifies the invoicing process, freeing up resources to focus on core business activities.
Accounts receivable: asset, liability, or equity?
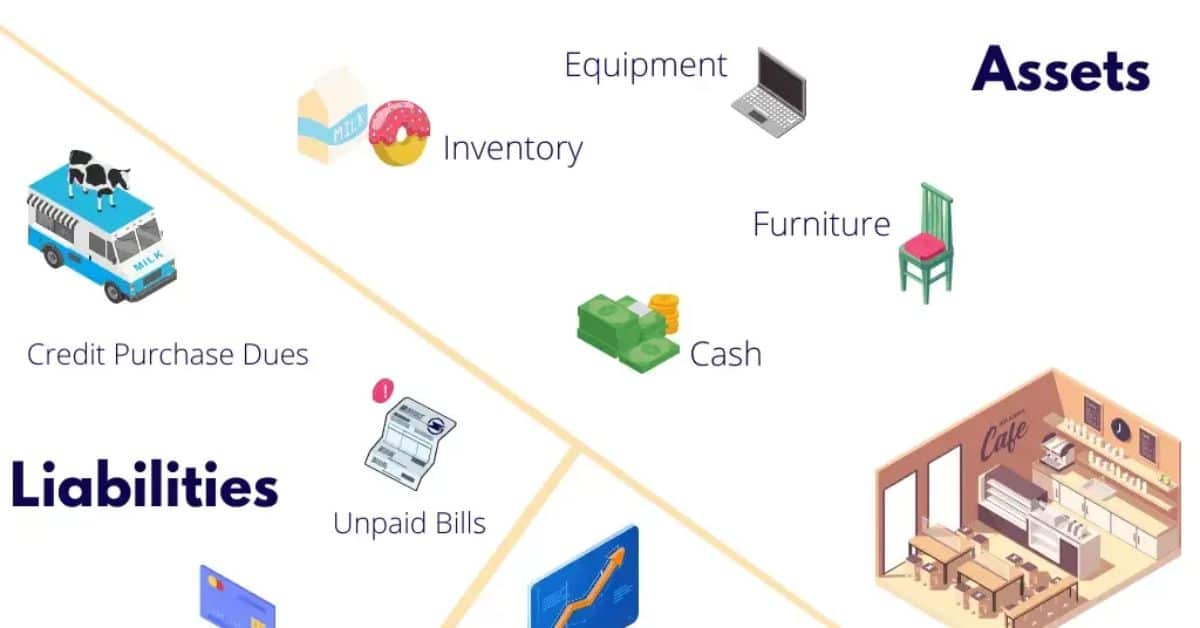
Accounts receivable are classified as assets on a company’s balance sheet, representing money owed by customers.
They contribute to a company’s liquidity and financial health, as they signify future cash inflows.
Unlike liabilities, which represent obligations, or equity, which reflects ownership, accounts receivable are assets awaiting collection.
Is net accounts receivable a current asset?
Yes, net accounts receivable is indeed classified as a current asset.
It represents the amount owed by customers after deductions for any doubtful accounts.
This figure reflects the portion of accounts receivable expected to be collected within the next year.
Net accounts receivable is crucial for assessing a company’s short-term liquidity and financial health.
Does accounts receivable count as a tangible asset?

Tangible assets are physical items with a clear value that can be easily measured, such as cash, inventory, vehicles, machinery, and buildings.
Accounts receivable represent money owed to a company by its customers, but they are generally classified as intangible assets due to their non-physical nature.
While accounts receivable are crucial for a company’s financial health, they are not considered tangible assets like cash or inventory.
Accounts payable: A Complete Overview
Accounts payable refers to the money a company owes to its suppliers, vendors, or creditors for goods or services received. It represents a liability for the company and is recorded on the balance sheet. Effective management of accounts payable is crucial for maintaining good relationships with suppliers and ensuring timely payments. Monitoring accounts payable helps businesses track their financial obligations and manage cash flow efficiently.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTION
Is accounts receivable an expense?
No, accounts receivable are not expenses; they are assets on a company’s balance sheet, representing money owed by customers for goods or services provided.
What is an example of accounts receivable?
An example of accounts receivable is when a company provides products or services to a customer on credit, creating a balance owed by the customer until payment is received.
How do companies handle uncollectible accounts?
Companies handle uncollectible accounts by setting aside a portion of their accounts receivable as an allowance for doubtful accounts to cover potential bad debts.
What is the impact of late payments on accounts receivable?
Late payments on accounts receivable can disrupt cash flow and increase the risk of bad debts, affecting a company’s financial stability and profitability.
Is an insurance an asset?
Yes, insurance can be considered an asset once it matures and the policyholder is credited with a lump sum or cash surrender value. Until maturity, insurance premiums paid are typically considered expenses.
SUMMARY
Accounts receivable (AR) serve as crucial assets for businesses, representing money owed by customers for goods or services provided. These outstanding balances contribute to a company’s financial health and liquidity, although they are not considered revenue until payment is received. Efficient management of AR offers insights into sales trends, customer behavior, and cash flow forecasting, aiding in informed decision making and improving overall financial well-being.
On the other hand, accounts payable (AP) represent the money a company owes to its suppliers or creditors for goods or services received. Effective management of AP is essential for maintaining good relationships with suppliers and ensuring timely payments to avoid disruptions in operations. Monitoring both AR and AP is vital for businesses to track their financial obligations accurately and manage cash flow efficiently, ultimately contributing to sustained growth and success.