Public finances are all about how governments handle their money. It is like managing a big wallet for a country, deciding how much to collect in taxes, how much to spend on things like schools and roads, and whether to borrow money when needed. Essentially, it is about making sure the government has enough funds to provide essential services and support the economy.
In simpler terms, public finances are the financial affairs of a nation’s government. They include everything from collecting taxes and managing spending to dealing with debts. By carefully balancing income and expenses, governments aim to meet the needs of their citizens and maintain economic stability.
Components of Public Finance

Components of public finance include activities like collecting taxes, planning budgets, making government expenditures, and managing deficits or surpluses. It is all about how governments raise and spend money to support society and the economy. The main components include:
Tax collection
Tax collection is a vital aspect of public finance, serving as the primary source of government revenue. It involves levying various types of taxes on individuals, businesses, and goods/services to fund public expenditures like infrastructure, education, and healthcare.
Taxes are essential for financing government operations and providing public services to citizens. They come in various forms, such as income tax, sales tax, property tax, and tariffs, each contributing to the overall revenue pool that supports the functioning of the government and the welfare of society.
Budget
A budget is a financial plan that outlines a government’s anticipated expenditures for a specific period, usually one fiscal year. It serves as a crucial tool for allocating resources to different sectors and programs, ensuring that taxpayer money is used efficiently and effectively.
In the United States, the budget process involves several steps, beginning with the president submitting a budget request to Congress. Subsequently, the House of Representatives and the Senate work on creating bills that address different aspects of the budget. Once these bills are approved by both chambers of Congress and signed into law by the president, they shape the government’s financial priorities for the upcoming fiscal year.
Expenditures
Expenditures represent the money spent by the government on goods, services, and programs to meet public needs and fulfill its responsibilities. These include investments in infrastructure, healthcare, education, defense, social welfare, and administrative expenses necessary for governance.
The government carefully allocates expenditures based on its priorities, policy objectives, and available resources. Through responsible spending decisions, it aims to enhance public services, promote economic growth, and improve the overall well-being of citizens while ensuring fiscal sustainability.
Deficit/Surplus
The deficit occurs when a government’s spending exceeds its revenue in a given period, resulting in a shortfall that needs to be financed through borrowing. Conversely, a surplus occurs when the government’s revenue exceeds its spending, allowing for savings or debt repayment.
Deficits and surpluses play a crucial role in shaping a government’s fiscal health and economic stability. While deficits may indicate excessive spending or revenue shortfalls, surpluses can signal prudent financial management and provide resources for future investments or debt reduction.
National Debt
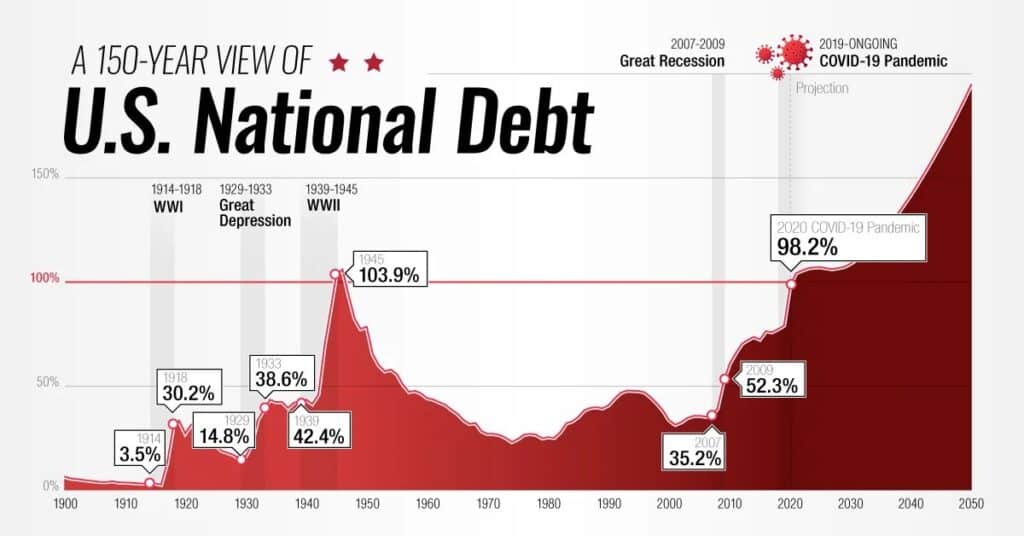
National debt refers to the total amount of money that a government owes to creditors, resulting from deficits incurred over time. It encompasses both domestic and foreign debt, accumulated through borrowing to cover budget shortfalls.
The national debt is a critical economic indicator reflecting a government’s financial health and its ability to meet debt obligations. It is influenced by factors such as government spending, revenue generation, and interest rates, with implications for economic stability and future generations’ financial burden.
Also Read: How Do I Disable Pof Account
Managing Public Finance
Managing public finance involves overseeing the collection of taxes, allocation of government expenditures, and management of deficits to ensure fiscal responsibility and economic stability. It requires careful planning, monitoring, and decision-making to effectively utilize public funds for the benefit of society.
Key aspects of managing public finance include creating budgets that prioritize spending on essential services such as education, healthcare, infrastructure, and social welfare. Additionally, it involves implementing policies to generate revenue through taxation while minimizing deficits and national debt.
By maintaining transparency, accountability, and efficiency in financial management, governments can promote economic growth, address societal needs, and uphold public trust in the management of public funds. Overall, effective management of public finance is essential for promoting the well-being and prosperity of a nation’s citizens.
Revenue and Expenditures
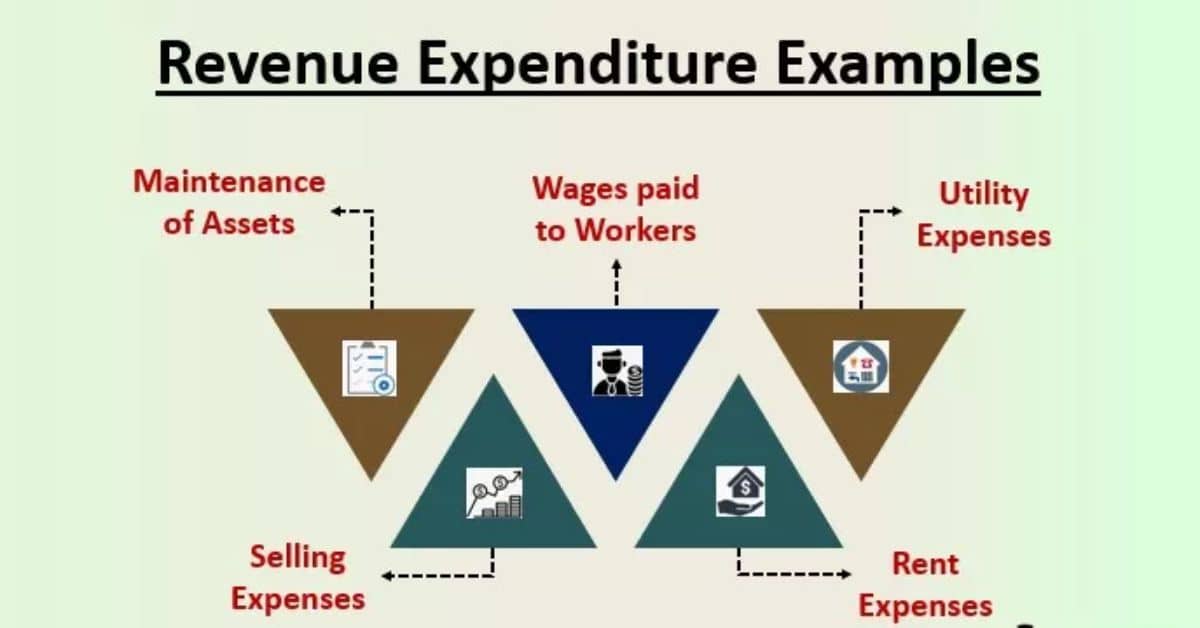
Below is a list of some of the most common revenues and expenditures in the world of public finance.
Revenue / Taxes
Income tax encompasses both personal and corporate taxes, levied on individuals’ earnings and corporations’ profits, respectively.
Property tax is assessed based on the value of real estate owned by individuals or businesses and is a primary revenue source for local governments.
Sales tax is a consumption tax imposed on the sale of goods and services at the point of purchase, collected by businesses and remitted to the government.
Value Added Tax (VAT) is a consumption tax levied on the value added at each stage of production or distribution, providing revenue for governments.
Import duties, also known as tariffs, are taxes imposed on goods imported into a country, designed to protect domestic industries and generate revenue.
Estate tax, or inheritance tax, is levied on the transfer of property or assets upon an individual’s death, with the tax rate based on the value of the estate.
Expenses
Health care refers to the provision of medical services and treatments to individuals, often funded through government programs, private insurance, or a combination of both.
Employment insurance provides financial support to individuals who are temporarily unemployed or unable to work due to specific circumstances, such as illness or maternity leave.
Pensions are retirement benefits provided to individuals after they reach a certain age or fulfill specific eligibility criteria, offering financial security in their later years.
Education encompasses the funding and provision of schooling and educational resources, including primary, secondary, and tertiary education, to support individuals’ learning and development.
Defense, often focused on military spending, involves the allocation of funds to support national security measures, including the armed forces, defense equipment, and strategic operations.
Infrastructure refers to the essential physical structures and facilities necessary for the functioning of society, such as roads, bridges, utilities, and public transportation systems, funded through government investments and public-private partnerships.
Additional Resources
Accounting for Income Taxes” explores the methods and regulations companies use to report their tax obligations in financial statements, addressing complex issues in corporate accounting.
Top Accounting Scandals” delves into infamous cases of financial misconduct and fraud, shedding light on the consequences of unethical practices in the corporate world.
Finance Salary Guide” provides insights into compensation trends and salary expectations for professionals working in the finance industry, aiding individuals in making informed career decisions.
War Bonds” discusses the issuance and impact of government-issued bonds during times of war, highlighting their role in financing military operations and stimulating economic activity.
Explore additional economics resources to further your understanding of various financial topics and industry insights.
How to Work in Public Finance

Working in public finance involves understanding government budgeting, taxation, and expenditure management to support societal needs and economic growth.
Individuals pursuing careers in public finance typically require education in economics, finance, or public administration, with opportunities ranging from entry-level positions to executive roles.
Earning a bachelor’s degree in finance or a related field is often the starting point for a career in public finance, providing foundational knowledge in economic principles and financial management.
Advanced degrees, such as a Master of Public Administration (MPA), offer specialized training in public finance, preparing individuals for leadership positions and policymaking roles in government agencies.
Also Read: Ally Permanent Life Insurance
How to Pursue a Career in Public Finance
To pursue a career in public finance, start with a bachelor’s degree in finance or related fields. Consider advanced degrees like an MPA and gain experience through internships for better opportunities.
Education:
Earn a bachelor’s degree in finance, economics, or related fields to establish foundational knowledge essential for a career in public finance.
Advanced Degrees:
Consider pursuing advanced degrees like a Master of Public Administration (MPA) to gain specialized training and expertise in public finance and administration.
Internships and Certifications:
Seek internships and obtain certifications to gain practical experience and enhance qualifications, preparing for roles in public finance.
Networking:
Build professional networks by connecting with individuals in the public finance sector, including professionals in government agencies, non-profit organizations, and consulting firms.
Job Exploration:
Explore diverse job opportunities in government agencies, non-profit organizations, and consulting firms to find roles aligned with career aspirations and interests.
Frequently asked question
Which is the biggest source of public finance?
The biggest source of public finance is taxes, including income tax, property tax, sales tax, and others, which provide revenue for government operations and services.
What is public finance accounting?
Public finance accounting involves managing and reporting government financial transactions, assets, and records to ensure effective decision-making, control, and transparency in the use of public funds
What are the types of finance?
Types of finance include public finance, corporate finance, and personal finance, each focusing on managing finances at different levels government, business, and individual
Why does public finance matter?
Public finance matters because it enables governments to fund essential services and infrastructure, manage economic stability, and address societal needs through effective allocation of financial resources.
What is the classical approach to public finance?
The classical approach to public finance emphasizes government roles in providing public goods, ensuring income distribution, and stabilizing the economy, often through limited intervention and laissez-faire policies.
What are the examples of public finance
Examples of public finance include funding for healthcare, education, defense, infrastructure, and social welfare programs, financed through taxes, borrowing, and government revenues.
Summary
Public finances encompass the management of a government’s revenue, expenditures, and debt through various institutions. They involve collecting taxes, creating budgets, making expenditures, and managing deficits or surpluses to ensure effective governance and economic stability.
The components of public finances include tax collection, budgeting, expenditures on public services and infrastructure, and managing deficits through borrowing. These finances play a crucial role in funding essential services, supporting societal needs, and shaping economic policies to promote growth and welfare.